Announcements
Circular economy isn’t just a buzzword — it’s a quiet revolution reshaping how we produce, consume, and rethink our relationship with resources. Instead of the outdated take-make-dispose model, it’s all about reusing, recycling, and getting smarter with what we already have.
The idea is simple: less waste, more efficiency. But the ripple effects go far beyond the environment. Businesses are innovating, economies are evolving, and opportunities are opening up for those ready to adapt.
Curious why major brands are shifting gears and how this shift might impact your own world? Keep reading and see how the circular economy is changing the game.
Announcements
Understanding the Circular Economy
The circular economy is an innovative approach that redefines our concepts of production and consumption. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a ‘take, make, dispose’ model, the circular economy emphasizes sustainability by ensuring that all resources are used efficiently and minimized in waste.
This approach is crucial for addressing environmental issues such as pollution and resource depletion.
Announcements
Key Concepts of the Circular Economy
One of the core ideas of the circular economy is to keep products, components, and materials in use for as long as possible. This is achieved through strategies like recycling, reusing, and refurbishing materials, which not only reduces the ecological footprint but also can lead to economic benefits.
Life Cycle Thinking
A vital component of the circular economy is understanding the life cycle of a product. Life cycle thinking considers every stage of a product’s existence—from raw material extraction to production, use, and eventual disposal. By analyzing each phase, businesses can identify opportunities to reduce waste and enhance sustainability.
Engagement of Stakeholders
For the circular economy to thrive, collaboration among various stakeholders is essential. This includes businesses, consumers, and governments working together to create systems that support sustainable practices. Engagement can lead to innovative solutions and increased efficiency across sectors.
Real-World Impact
The circular economy aims to mimic natural systems where waste is eliminated, and resources are regenerated. By shifting our perspective on waste and resource management, we not only work towards a healthier planet but also encourage economic growth and job creation.
Principles of Circular Design
The principles of circular design are essential for creating products that fit into the circular economy framework. These principles focus on sustainability and aim to minimize waste throughout a product’s life cycle.
1. Design for Longevity
Creating products that last is fundamental. This means using durable materials and building items that can withstand wear and tear. Products should be designed with the intention of being used for as long as possible, reducing the need for replacements.
2. Design for Repairability
Products should be easy to repair. Efficient repair processes mean that items can be fixed rather than discarded. Design features, such as removable parts and clear instructions, encourage users to consider repairs before replacements.
3. Design for Reusability
Emphasizing reusability is vital. Products should have multiple uses or be easily adaptable for different functions. This helps extend their life and reduce waste, keeping materials in circulation longer.
4. Use of Sustainable Materials
Choosing materials that are renewable, biodegradable, or recycled helps combat resource depletion. Sustainable materials not only lessen environmental impacts but also improve the overall footprint of the product.
5. End-of-Life Considerations
Designers should consider what happens to a product at the end of its life. This includes making products easy to disassemble for recycling and providing guidance on responsible disposal. This principle ensures that materials can be reclaimed and reused.
Benefits of the Circular Economy
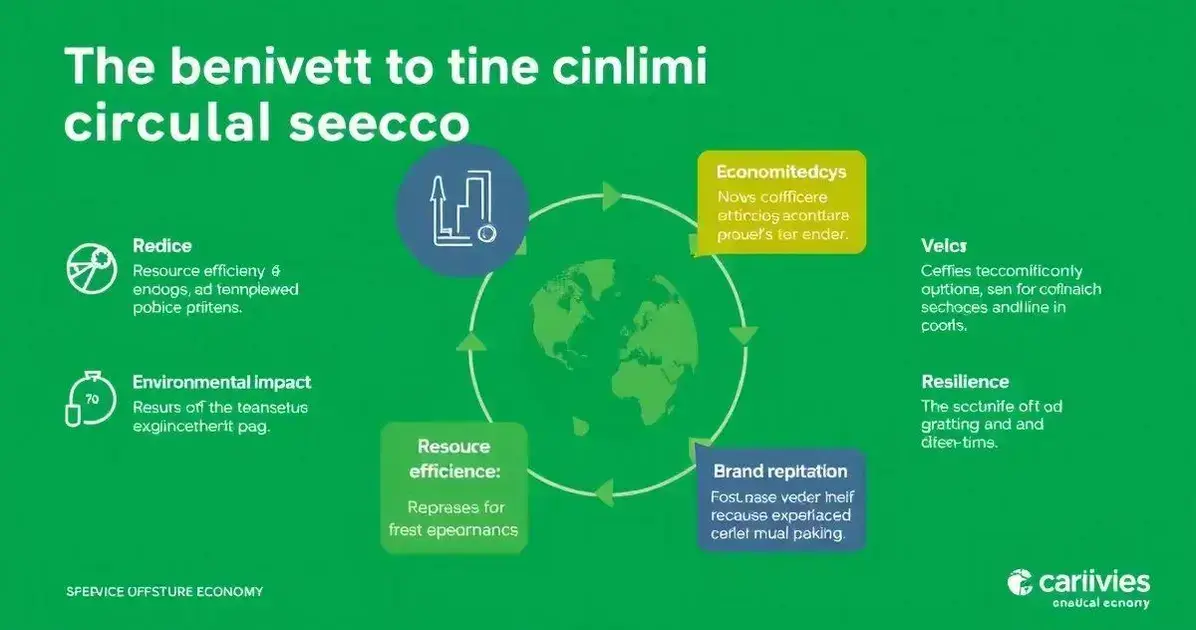
The circular economy offers numerous benefits that positively impact both the environment and the economy. By embracing this model, we can create a more sustainable future.
1. Resource Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of the circular economy is improved resource efficiency. By reusing materials and reducing waste, businesses can lower their costs and make better use of the resources available. This not only conserves materials but also minimizes the impact on the environment.
2. Economic Growth
The circular economy stimulates economic growth by encouraging innovation. New business models and solutions focused on sustainability create opportunities for job creation and investment. As companies adopt circular practices, they can discover new markets and revenue streams.
3. Reduced Environmental Impact
Implementing circular economy principles helps reduce pollution and the strain on natural resources. By keeping materials in use and designing with sustainability in mind, businesses contribute to less waste and a cleaner environment for future generations.
4. Enhanced Brand Reputation
Organizations that commit to sustainability and circular practices often enjoy an enhanced brand reputation. Consumers are increasingly looking for eco-friendly options, and companies that demonstrate a commitment to a circular economy can attract more customers and build loyalty.
5. Resilience to Supply Chain Disruptions
Using recycled and locally sourced materials can make businesses more resilient to supply chain disruptions. With a focus on sustaining resources within the local community, companies can reduce dependence on volatile global markets and enhance their overall stability.
Challenges in Implementing Circular Practices
Implementing circular practices presents several challenges that businesses must navigate. Recognizing these obstacles is crucial for effectively transitioning to a circular economy.
1. Initial Costs
Transitioning to a circular economy can involve significant upfront investments. Businesses may need to change their production processes, invest in new technologies, or train employees. These expenses can be daunting, particularly for small businesses.
2. Lack of Consumer Awareness
Many consumers are not fully aware of the benefits of circular products. Without proper education, they may resist change or prefer familiar linear options. Building consumer awareness and demand for circular products is vital for successful implementation.
3. Complex Supply Chains
Circular practices often require changes in supply chain management. Sourcing recycled materials, establishing take-back programs, and ensuring all partners are aligned can complicate operations. Businesses must coordinate effectively with suppliers to meet these new demands.
4. Regulatory Barriers
In some regions, existing regulations may not support circular initiatives. Policies favoring linear models can restrict innovation. Advocating for policy changes that promote circular practices is essential for overcoming these barriers.
5. Cultural Resistance
Shifting to a circular economy may face cultural resistance within organizations. Employees accustomed to traditional methods may be hesitant to adopt new practices. Engaging staff and demonstrating the benefits of change can help overcome this resistance.
Successful Circular Economy Examples
Many companies around the world are successfully embracing the circular economy. Here are some notable examples that showcase how businesses can thrive while promoting sustainability.
1. Interface
Interface, a leading carpet tile manufacturer, has committed to sustainability by implementing a closed-loop system. They recycle old carpet materials into new products and aim to become a carbon negative company by 2040. Their innovative approach not only reduces waste but also sets a standard in the flooring industry.
2. Philips
Philips has launched a circular lighting solution where they retain ownership of the lights. Customers pay for the service of light instead of purchasing the products. This model encourages the return of old products for recycling and promotes sustainable use of materials.
3. Patagonia
Patagonia is known for its commitment to the environment. They encourage customers to repair old gear instead of buying new products through their Worn Wear program. They also use recycled materials in their clothing lines, promoting sustainability and reducing waste.
4. IKEA
IKEA has embarked on a journey to become a circular business by 2030. They focus on using renewable and recycled materials in products. Additionally, they offer take-back services for old furniture, ensuring that materials are reused or recycled, rather than ending up in landfills.
5. Unilever
Unilever is invested in promoting a circular economy through their products and packaging. They aim to make all their plastic packaging recyclable, reusable, or compostable by 2025. Their commitment to sustainability helps reduce ocean plastic pollution and encourages responsible consumer behavior.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about the Circular Economy
What is the circular economy?
The circular economy is a model that focuses on sustainability by reusing materials, reducing waste, and ensuring resources are kept in use for as long as possible.
What are the benefits of the circular economy?
The circular economy offers benefits such as resource efficiency, economic growth, reduced environmental impact, enhanced brand reputation, and resilience to supply chain disruptions.
What are the principles of circular design?
Circular design principles include designing for longevity, repairability, reusability, using sustainable materials, and considering end-of-life scenarios.
What challenges do businesses face in implementing circular practices?
Businesses may face challenges such as initial costs, lack of consumer awareness, complex supply chains, regulatory barriers, and cultural resistance within organizations.
Can you provide examples of companies successfully implementing the circular economy?
Sure! Companies like Interface, Philips, Patagonia, IKEA, and Unilever have made significant strides in adopting circular practices and promoting sustainability in their operations.
How can I encourage my business to move towards a circular economy?
Start by analyzing your current practices, designing for sustainability, engaging stakeholders, and exploring innovative business models that prioritize resource reuse and waste reduction.







